USA Coalition vs. Russian Coalition: FDI and International Trade Analysis
https://www.rozen-bakher.com/monitoring-risks/30/03/2022
Published Date: 30 March 2022
COPYRIGHT ©2022-2024 ZIVA ROZEN-BAKHER ALL RIGHTS RESERVED
Rozen-Bakher, Z., USA Coalition vs. Russian Coalition: FDI and International Trade Analysis, Monitoring Risks by Dr. Ziva Rozen-Bakher, 30 March 2022, https://www.rozen-bakher.com/monitoring-risks/30/03/2022
Monitoring Risks by Dr. Ziva Rozen-Bakher
Analysing in-Depth Security & Political Risks and Economic & Strategic Risks
Rozen-Bakher, Z. Monitoring Risks by Dr. Ziva Rozen-Bakher https://www.rozen-bakher.com/monitoring-risks-1
Dr. Ziva Rozen-Bakher
Researcher in International Relations and Foreign Policy with a Focus on International Security alongside Military, Political and Economic Risks for Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) and International Trade
USA Coalition vs. Russian Coalition: FDI and International Trade Analysis, 30 March 2022
Since the start of the Ukraine war, the Sanctions-War has intensified between the USA Coalition vs. Russian Coalition (see Map 1 below), yet it is doubtful if all policy-makers understand the mechanism of sanctions/counter-sanctions, including the distinction between formal versus informal sanctions/counter-sanctions. Moreover, if we look at the data of FDI and International Trade (see Tables 1-2 below), then apparently, the quantity of FDI and Trade of the USA coalition is bigger than the Russian Coalition, but if we look at the data in-depth, then we get a more complicated picture because of the missing data among countries of the Russian Coalition that de-facto hides the activity of FDI and International Trade, and as a result, it also hides the informal counter-sanctions.
Missing Data/Delayed Data of FDI and International Trade
Non-Governmental Organisations (NGOs) like the World Bank (WB) and UNCTAD are collecting data about various indicators in order to compare different countries via the same indicators. Still, it is based on two principles: i) Countries should voluntarily provide the data to NGOs based on the standardisation of the indicator to allow comparison between different countries. However, if the data of a certain country are not aligned with the standardisation of a certain indicator, then the NGO does not publish the data, and it is mentioned as ‘Missing Data’. Hence, as shown in Appendix I below, if a country provided data from a few years earlier, then this data is mentioned in Appendix I as 'Delayed Data', while if a country decided to not provide the data to NGOs, then it is mentioned in Appendix I as 'Missing Data'.
Nevertheless, either if it is because of missing data or delayed data, the outcome is the same, namely there is 'Missing Data' in relation to some country. Hence, if we look at the countries that have missing data/delayed data on International Trade, then most of the countries belong to the Russian Coalition rather than to the USA Coalition. Importantly, from the coalition perspective, all the missing data/delayed data that belong to the USA coalition are related to small countries/territories of the USA coalition (e.g., Liechtenstein, Monaco and San Marino), while most of the missing data/delayed data that belong to the Russian coalition are related to big/significant countries of the Russian coalition, such as Cuba, Iran, North Korea, Syria, Turkmenistan, the United Arab Emirates, Bahrain, Libya, and Venezuela. Besides, if we look at the core of each coalition (see Map 2 below), then most of the countries with missing data/delayed data belong to the core of the Russian coalition. That means that each country with missing data that belongs to the Russia Coalition has more ability to carry out informal counter-sanctions because of the lack of transparency. Even a significant delay in providing data could give a time frame to manipulate the data in terms of counter-sanctions.
To summarise, the comparison of data of International trade and FDI between the USA coalition and the Russian coalition does not reflect the whole activity of the Russian coalition because 15 countries among the Russian coalition have missing data, while 28 countries have delayed data that may not reflect the current activity. Importantly, the missing data/delayed data reflect a lack of transparency, which creates the potential to carry out informal international trade and FDI that could serve as a tool for counter-sanctions or even as a tool for bypassing sanctions.
Formal versus Informal Sanctions/Counter-Sanctions
Considering the Missing Data/Delayed Data outlined above, we need to distinguish between Formal versus Informal Sanctions/Counter-Sanctions. Formal sanctions/counter-sanctions imposed by official authorities of countries via formal declarations about it, such as the formal sanctions imposed by the USA and the EU against Russia (e.g. Ban on oil imports from Russia to the USA), or vice versa, the formal counter-sanctions imposed by Russia against the West (e.g. Ban on the export of Russian commodities). However, informal sanctions/counter-sanctions are done without an official declaration about it, yet the outcome is the same as formal sanctions/counter-sanctions.
Counter-Sanctions vs. Bypassing Sanctions
Regardless of the above, we need to distinguish between counter-sanctions and bypassing sanctions. Counter-sanctions are imposed against those who were imposed sanctions in the first place, while ‘Bypassing Sanctions’ refers to avoiding sanctions via the help of a third party. Bypassing sanctions could be carried out via informal channels, so in this case, it reflects informal trade that does not appear in the official data of a country. Thereby, countries with Missing Data/Delayed Data of International Trade can more easily engage in helping to bypass sanctions. Nevertheless, bypassing sanctions could also be carried out by formal channels, yet neutral third parties are needed to serve as ‘middlemen’. For example, a German exporter could export its goods to an importer in Turkey, and after that, an exporter in Turkey could export the same goods to an importer in Russia. This mechanism of bypassing sanctions, either formally or informally, explains why the sanctions are not effective, which is opposite to the common view of many decision-makers.
Mechanism of Informal Sanctions/Counter-Sanctions
Informal sanctions/counter-sanctions could be carried out at the country level via export, import, FDI Inward, and FDI Outward (see Appendix II below), as follows:
Export. Each coalition could find new importers for its export among the members of its coalition in order to create sanctions/counter-sanctions via export. Thus, under this informal mechanism, the allocation of exports leads de-facto to sanction/counter-sanctions, without formally declaring about it.
Import. Each coalition could find new exporters for its import among the members of its coalition in order to create sanctions/counter-sanctions via import. Thus, under this informal mechanism, the allocation of imports leads de-facto to sanction/counter-sanctions, without formally declaring about it.
FDI Inward. In FDI bids, each coalition could give priority to countries from its coalition. That's can also apply in privatizations and even in some cases of M&As.
FDI Outward. In FDI outward, each coalition could give priority to investments in host countries from its coalition.
To conclude, my analysis indicates that the war-sanctions between the USA Coalition and the Russian Coalition will lead to a transformation in the global order. It will create two coalitions that will compete against each to win the war-sanctions (see Appendix III below). The USA coalition has an advantage in market size, while the Russian Coalition has advantages in energy, the number of countries that belong to its coalition, and the ability to carry out informal counter-sanctions and even to bypass sanctions. It's going to be a tough war!
Map 1. Sanctions against Russia
Table 1. Export, Import, FDI Inward, FDI Outward: USA Coalition vs. Russian Coalition, sorted by a-b
Map 2. Core of USA Coalition versus Core of Russian Coalition
Table 2. Export, Import, FDI Inward, FDI Outward: USA Coalition vs. Russian Coalition, sorted by Coalitions
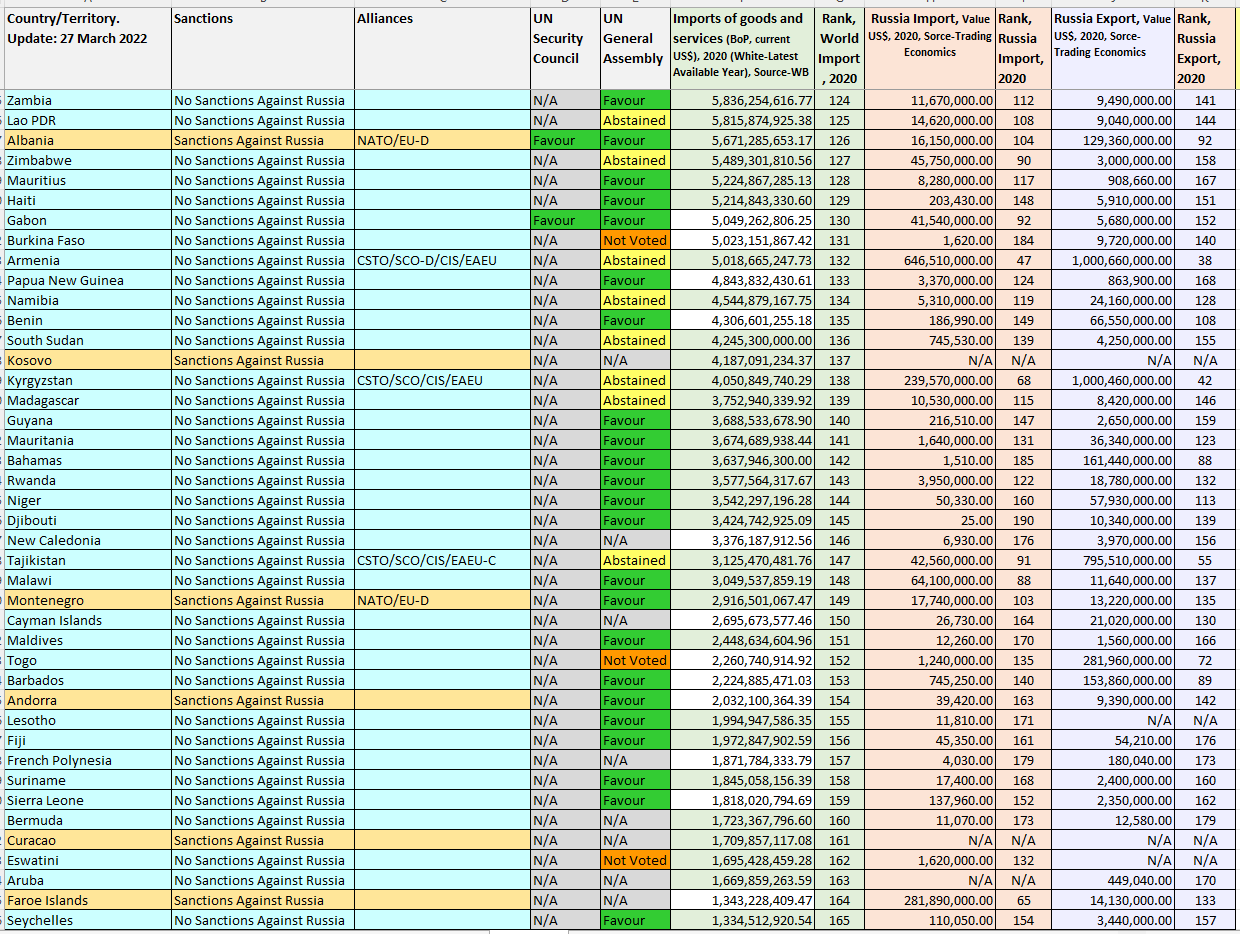
Appendix I. Missing Data/Delayed Data of Trade and FDI: USA Coalition vs. Russian Coalition
Missing Data/Delayed Data of Trade and FDI: USA Coalition vs. Russian Coalition
Appendix II. Rank of Exports, Imports, FDI Inwards, and FDI Outwards: USA Coalition vs. Russian Coalition, sorted by Total of Each Rank (Higher to Lower)
Export Rank: USA Coalition vs. Russian Coalition
Import Rank: USA Coalition vs. Russian Coalition
FDI Inward Rank: USA Coalition vs. Russian Coalition
FDI Outward Rank: USA Coalition vs. Russian Coalition
Appendix III. Alliances: USA Coalition vs. Russian Coalition