Impact of Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) on Labour Markets: Nationalism-Mercantilism versus Trade Liberalism
https://www.rozen-bakher.com/monitoring-risks/05/07/2023
Published Date: 05 July 2023
COPYRIGHT ©2022-2024 ZIVA ROZEN-BAKHER ALL RIGHTS RESERVED
Rozen-Bakher, Z., Impact of Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) on Labour Markets: Nationalism-Mercantilism versus Trade Liberalism, Monitoring Risks by Dr. Ziva Rozen-Bakher, 05 July 2023, https://www.rozen-bakher.com/monitoring-risks/05/07/2023
Monitoring Risks by Dr. Ziva Rozen-Bakher
Analysing in-Depth Security & Political Risks and Economic & Strategic Risks
Rozen-Bakher, Z. Monitoring Risks by Dr. Ziva Rozen-Bakher https://www.rozen-bakher.com/monitoring-risks-1
Dr. Ziva Rozen-Bakher
Researcher in International Relations and Foreign Policy with a Focus on International Security alongside Military, Political and Economic Risks for Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) and International Trade
Impact of Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) on Labour Markets: Nationalism-Mercantilism versus Trade Liberalism, 05 July 2023
Background
Policymakers always have an ambivalent attitude regarding the impact of Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) on national labour markets. FDI can lead to the creation of new jobs, but at the same time, it can lead to the relocation and elimination of jobs (see Figure 1 below). Under this trade-off, any government struggles to find the ‘optimal FDI-labour market policy’ that will encourage FDI yet without harming the national labour market or the national strategic interests. That may be seen as an impossible task, especially when an unprecedented economic crisis strikes the national labour market because of a national crisis, a regional crisis or even a global crisis, such as the global financial crisis that started in 2008 and had hit labour markets worldwide for 10 years, yet when the labour markets had started to recover, then came the Coronavirus, which also impacted the labour markets. Decision-making under crisis circumstances is always challenging because of the fear that urgent decisions may result in dramatic mistakes that may backfire on the bad situation instead of improving it.
Regardless of crises, the aging era changed dramatically the labour markets at the global level, as I presented in my published paper: Rozen-Bakher, Z. (2020). The Raising of the Normal Retirement Age (NRA) in the Aging Era in the Advanced Countries: The Dilemma between Securing the Stability of the Pension System versus the Risk of Increasing Unemployment. Policy Studies, 41(6), 641-662. https://doi.org/10.1080/01442872.2018.1554805. The conceptual model of this published paper (see Figure 2 below) clearly presents how the combination of Aging and Relocation of Jobs dramatically impacts the labour markets worldwide, regardless of crises and other factors. Thereby, any government worldwide has started to act in a mode of ‘save yourself’, namely struggling to find the ‘miracle employment solution’ for its citizens, including weighing how the national Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) policy can create new jobs or, vice versa, can reduce the relocation and elimination of jobs. That leads governments to choose between two opposite policies, namely Nationalism-Mercantilism versus Trade Liberalism, as I presented in my research paper: Rozen-Bakher, Z. Restrictions on International Trade and Foreign Direct Investment (FDI): Nationalism-Mercantilism versus Trade Liberalism. Research Paper, PD9. https://www.rozen-bakher.com/unpublished-research-papers/pd9. Nevertheless, examining and analysing the impact of FDI on labour markets in a crisis period allows us to understand how the crisis impacts the labour markets, but it may worsen the confusion of decision-makers because it does not necessarily provide a clear understanding of which policy is needed for recovery and prosperity, while exploring the impact of FDI on labour markets in a non-crisis period may provide a better understanding of how to navigate the labour markets under the whole current challenging circumstances. Hence, I choose to examine the impact of FDI on labour markets in a non-crisis period. To fulfil this objective, I examined the impact of FDI on labour markets worldwide in the era of liberalisation and pre-global crises, as I presented in the next sections.
Figure 1. Impact of FDI Inwards versus FDI Outwards on Labour Markets
Figure 2. Conceptual Model of Labour Market in the Aging Era
Rozen-Bakher, Z. (2020). The Raising of the Normal Retirement Age (NRA) in the Aging Era in the Advanced Countries: The Dilemma between Securing the Stability of the Pension System versus the Risk of Increasing Unemployment. Policy Studies, 41(6), 641-662. https://doi.org/10.1080/01442872.2018.1554805
Research Model and Theoretical Background
In light of the above, Figure 3 presents the Research Model of the study.
Figure 3. Research Model
Theoretical Background:
To understand in-depth the Research Model, Please see my additional relevant Research Papers that also include research literature on this topic:
Rozen-Bakher, Z. (2021). Restrictions on International Trade and Foreign Direct Investment (FDI): Nationalism-Mercantilism versus Trade Liberalism. Unpublished Research Paper, PD9. https://www.rozen-bakher.com/unpublished-research-papers/pd9
Rozen-Bakher, Z. (2020). The Raising of the Normal Retirement Age (NRA) in the Aging Era in the Advanced Countries: The Dilemma between Securing the Stability of the Pension System versus the Risk of Increasing Unemployment. Policy Studies, 41(6), 641-662.
Rozen-Bakher, Z. (2018). Labour Productivity in M&As: Industry Sector vs. Services Sector. The Service Industries Journal. 38(15-16), 1043-1066.
Rozen-Bakher, Z. (2017). Impact of Inward and Outward FDI on Employment: The Role of Strategic Asset-Seeking FDI. Transnational Corporations Review, 9(1), 16-30.
Rozen-Bakher, Z. (2011). Multinational Enterprises (MNEs) in the Global Era: The Impact of Location Factors ─ Economic, Political, Technological, Cultural and Labour Market Policy ─ on Inward and Outward Foreign Direct Investment (FDI), and the implications of FDI inward and FDI outward on Labour Markets. University of Haifa. Hebrew. Supervisors: Cohen, A. & Weber, Y. https://www.rozen-bakher.com/s/Dissertation-final-Ziva-Rozen-Bachar.pdf
Rozen-Bakher, Z. (2021). FDI’s Unresolved Risk of Cultural Distance - Alternatives Measuring to National Cultural Values: Language Distance, Religion Distance, and Cultural Openness. Unpublished Research Paper, PD7. https://www.rozen-bakher.com/unpublished-research-papers/pd7
Rozen-Bakher, Z. (2004). The Impact of Mergers & Acquisitions (M&As) on Employment and Labour Productivity: M&As with Labour Unions versus M&As without Labour Unions. University of Haifa. Hebrew. Supervisor: Cohen, A. https://www.rozen-bakher.com/s/MA-Dissertation-Rozen-Bakher-Z-_2004.pdf
Rozen-Bakher, Z. (2021). Are Multinational Enterprises’ (MNEs) Theories explained the reality of Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) and International Trade in the 21st Century?. Unpublished Research Paper, PD2. https://www.rozen-bakher.com/unpublished-research-papers/pd2
Rozen-Bakher, Z. (2021). A Regime Type as a Location Factor of FDI: Democracy, Communism, Absolute Monarchy, Religious Regime, and Military Regime. Unpublished Research Paper, PD5. https://www.rozen-bakher.com/unpublished-research-papers/pd5
Rozen-Bakher, Z. (2021). Technological Location Factors of Foreign Direct Investment (FDI): R&D Expenditure, Technological Strategic Assets, Technical Labour, and ICT Infrastructure. Unpublished Research Paper, PD6. https://www.rozen-bakher.com/unpublished-research-papers/pd6
Rozen-Bakher, Z. (2021). Legal Distance in FDI - The Differences in the Legal Location Factors between the Home country, Host country, and International Law: Risk Analysis. Unpublished Research Paper, PD8. https://www.rozen-bakher.com/unpublished-research-papers/pd8
Rozen-Bakher, Z. (2021). Restrictions on International Trade and Foreign Direct Investment (FDI): Nationalism-Mercantilism versus Trade Liberalism. Unpublished Research Paper, PD9. https://www.rozen-bakher.com/unpublished-research-papers/pd9
Rozen-Bakher, Z. (2021). Risk Analysis of Entry Modes: Comparison of Greenfield & Brownfield, Mergers & Acquisitions, Joint Ventures, Export, Licensing, and Franchising. Unpublished Research Paper, PD12. https://www.rozen-bakher.com/unpublished-research-papers/pd12
Rozen-Bakher, Z. (2018). How National Cultural Differences Influence M&A Success in Cross-Border M&As?. Transnational Corporations Review, 10(2), 131-146.
Rozen-Bakher, Z. (2018). Comparison of Merger and Acquisition (M&A) Success in Horizontal, Vertical and Conglomerate M&As: Industry Sector vs. Services Sector. The Service Industries Journal, 38 (7-8), 492-518.
Methodology
Figure IV presents the Methodology of the study in order to examine the impact of FDI on the labour market in the non-crisis era, so accordingly the sample includes 191 countries during the years 1992-2007. Table 1 presents the Research Variables of the study, including its Indicators, Databases, and Data Sources. Besides, the study includes four levels of comparison, as follows:
FDI Inward versus FDI Outward.
All countries versus Advanced Countries versus Emerging & Developing Countries.
Short-run Analysis versus Trend Analysis versus Long-run Analysis.
Entry mode: Mergers & Acquisitions versus Greenfields.
Figure 4. Methodology
Table 1. Research Variables: Indicators, Databases, and Data Sources
Analysis and Concluding Remarks
The results of the study (see the Result Section below) did not confirm the common belief among many governmental decision-makers that FDI in non-crisis periods increases unemployment. However, FDI leads to a decrease in Employment in Agriculture mainly in Advanced Countries, while it increases Employment in Industry in Emerging and Developing Countries, yet FDI increases Employment in Services in Advanced Countries with a prospect for the same positive direction in Emerging and Developing Countries. For in-depth understanding, please see my research paper on ‘Sectoral Employment Shift’: Rozen-Bakher, Z. (2017). Impact of Inward and Outward FDI on Employment: The Role of Strategic Asset-Seeking FDI. Transnational Corporations Review, 9(1), 16-30. https://doi.org/10.1080/19186444.2017.1290919, as well as my research paper that compares the Industry Sector versus Services Sector among FDI-M&As: Rozen-Bakher, Z. (2018). Comparison of Merger and Acquisition (M&A) Success in Horizontal, Vertical and Conglomerate M&As: Industry Sector vs. Services Sector. The Service Industries Journal, 38 (7-8), 492-518. https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/10.1080/02642069.2017.1405938. Notably, M&As is one of the Entry Modes of FDI as I explained in my research paper that compares the risks of the Entry Modes of FDI versus the Entry Modes of International trade: Rozen-Bakher, Z. (2021). Risk Analysis of Entry Modes: Comparison of Greenfield & Brownfield, Mergers & Acquisitions, Joint Ventures, Export, Licensing, and Franchising. Research Paper, PD12. https://www.rozen-bakher.com/research-papers/pd12
Nevertheless, the big benefit of FDI is for Labour Productivity and Educated Labour, especially in Emerging and Developing Countries. However, the picture becomes more complicated when we take into account the Location Factors (see Figure 3-4 above), namely some Location Factors have a positive impact on Labour Market, while others have a negative impact, yet the big challenge is when a Location Factor has a positive impact on one indicator of Labour Market, while a negative impact on another indicator of Labour Market, resulting in a trade-off. Therefore, each country should look at which location factors are more relevant/important to the country and how they impact each indicator of the labour market in trying to offset the trade-off.
Hence, the study, in general, concludes that a policy of Nationalism-Mercantilism may backfire on FDI and Labour Market in the Long-Run and even in the Mid-Run, while a policy of Trade Liberalism will benefit FDI and Labour Market, especially when specific Location Factors used as ‘engines’ for encouraging FDI-Labour Market. For in-depth understanding about Nationalism-Mercantilism policy versus Trade Liberalism policy, please see my research paper: Rozen-Bakher, Z. Restrictions on International Trade and Foreign Direct Investment (FDI): Nationalism-Mercantilism versus Trade Liberalism, Research Paper, PD9. https://www.rozen-bakher.com/research-papers/pd9, as well as my additional research paper: Rozen-Bakher, Z. Are Multinational Enterprises’ (MNEs) Theories explained the reality of Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) and International Trade in the 21st Century?. Research Paper, PD2. https://www.rozen-bakher.com/research-papers/pd2.
Results
Summary List of Results
Descriptive Statistics and Correlations Matrix - All countries, Advanced Countries, Emerging & Developing Countries
Comparing Mean by Year: Location Factors, FDI and Labour Markets - All countries, Advanced Countries, Emerging & Developing Countries
The Impact of Location Factors on FDI (H1, Path a): FDI Inward Vs. FDI Outward
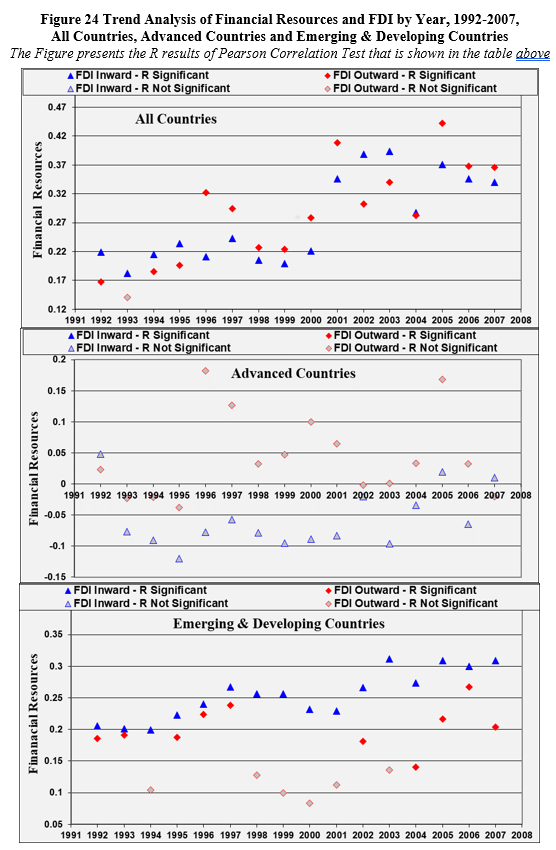
Short-Run Analysis and Trend Analysis: The Impact of Location Factors on FDI (H1, Path a) - All countries, Advanced Countries, Emerging & Developing Countries
Short-run Analysis of Dominant Location Factors: The Impact of Location Factors on FDI (H1, Path a) - All Countries
Long-Run Analysis: The Impact of Location Factors on FDI (H1, Path a) - All countries, Advanced Countries, Emerging & Developing Countries
Long-run Analysis of Dominant Location Factors: The Impact of Location Factors on FDI (H1, Path a) - All countries, Advanced Countries, Emerging & Developing Countries
The Impact of FDI Inward Vs. FDI Outward on Labour Market (H2, Path b): Short-run Analysis, Trend Analysis and Long-Run Analysis - All countries, Advanced Countries, Emerging & Developing Countries
The Impact of Location Factors on Labour Markets: The Mediation Role of FDI (H3, Path C, Path a+b)
Long-run Analysis: The Impact of Location Factors on Labour Markets and the Mediation Role of FDI (H3, Path C, Path a+b) - All countries, Advanced Countries, Emerging & Developing Countries
Long-run Analysis of Dominant Location Factors: The Impact of Location Factors and the Mediation Role of FDI on Labour Markets (H3) - All Countries, Advanced Countries, Emerging & Developing Countries
The Role of Entry Mode of FDI in Host Country versus Home Country: International Mergers & Acquisitions versus Greenfields
Long-Run Analysis: The Impact of Location Factors on Entry Modes of FDI (H4, path a) - All countries, Advanced Countries, Emerging & Developing Countries
Long-run Analysis of Dominant Location Factors: The Impact of Location Factors on Entry Modes of FDI (H4, Path a) - All countries, Advanced Countries, Emerging & Developing Countries
Long-run Analysis: The Impact of Location Factors on Labour Markets and the Mediation Role of Entry Modes of FDI (H6, Path C, Path a+b) - All countries, Advanced Countries, Emerging & Developing Countries
Long-run Analysis: The Impact of Location Factors on Labour Markets and the Mediation Role of M&As (H6, Path C, Path a+b) - All countries, Advanced Countries, Emerging & Developing Countries
Long-run Analysis of Dominant Location Factors: The Impact of Location Factors and Greenfields on Labour Markets (H6) - All Countries, Emerging & Developing Countries